
Here at The Next Platform, we’ve touched on the convergence of machine learning, HPC, and enterprise requirements looking at ways that vendors are trying to reduce the barriers to enable enterprises to leverage AI and machine learning to better address the rapid changes brought about by such emerging trends as the cloud, edge computing and mobility.
At the SC17 show in November 2017, Dell EMC unveiled efforts underway to bring AI, machine learning and deep learning into the mainstream, similar to how the company and other vendors in recent years have been working to make it easier for enterprises to adopt HPC techniques for their environments. For Dell EMC, that means in part doing so through bundled, engineered systems.
IBM has strategies underway, including through the integration of its PowerAI deep learning enterprise software with its Data Science Experience. Both offerings are aimed at making it easier for enterprises to embrace advance AI technologies and for developers and data scientists to develop and train machine learning models. Software vendors like SAP and Microsoft similarly are easing the way for enterprise adoption of AI and machine learning techniques.
Google has been a vocal proponent of the idea of democratizing AI by making it easier for mainstream businesses to use. As we outlined last year, Google sees its capabilities in AI, machine learning and deep learning as a competitive advantage against larger hyperscale players like Amazon Web Services and Microsoft Azure in the highly competitive cloud computing arena and a key way of enticing enterprises to the Google Cloud Platform to help them manage, analyze and leverage the rapidly mounting data to more quickly and effectively build products and services that their customers can use. Google in 2016 created a machine learning unit within its Cloud Platform business and rolled out a series of APIs for such jobs as natural language, language translation and vision recognition. The hyperscaler also brought in Fei-Fei Li, at the time the director of Stanford University’s Artificial Intelligence Lab and the Stanford Vision Lab, to head up the new machine learning group.
Last year, Google’s AI researchers rolled out the Google Cloud Machine Learning Engine to make it easier for those developers with expertise in machine learning to build machine learning models for data of any size and made such APIs as Vision, Speech, Translation and Dialogflow available to be built atop pre-trained models to bring greater scale and speed to business workloads. According to Google researcher’s, the company’s Kaggle community of data scientists and machine learning experts has passed a million members and Box, Rolls Royce Marine and Kewpie are among the 10,000-plus businesses using Google Cloud AI services.
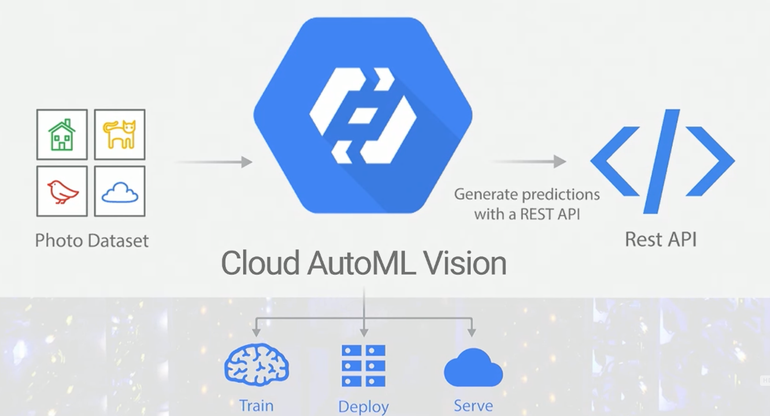
However, relatively few businesses have the skill or money to take full advantage of the capabilities in AI and machine learning, and this month Google is taking another step in addressing this gap. The company this month introduced Cloud AutoML, a plan to make machine learning services within the Google Cloud more easily accessible to both those developers with expertise in AI and engineers with fewer skills build AI systems.
“Currently, only a handful of businesses in the world have access to the talent and budgets needed to fully appreciate the advancements of ML and AI,” Li, chief scientist for the Cloud AI unit at Google, and Jai Li, head of R&D at Cloud AI noted. “There’s a very limited number of people that can create advanced machine learning models. And if you’re one of the companies that has access to ML/AI engineers, you still have to manage the time-intensive and complicated process of building your own custom ML model. While Google has offered pre-trained machine learning models via APIs that perform specific tasks, there’s still a long road ahead if we want to bring AI to everyone. To close this gap, and to make AI accessible to every business, we’re introducing Cloud AutoML. Cloud AutoML helps businesses with limited ML expertise start building their own high-quality custom models by using advanced techniques like learning2learn and transfer learning from Google. We believe Cloud AutoML will make AI experts even more productive, advance new fields in AI and help less-skilled engineers build powerful AI systems they previously only dreamed of.”
The company will start with Cloud AutoML Vision for creating machine learning models for image recognition and analysis. Through the service, users will be able to upload their labeled or unlabeled images, and then let Google create the machine learning model based on those images. After uploading the dataset of images, the user presses the “train” button on the UI to train a custom model on the dataset. After training, analysis and statistics are presented in the UI. Predictions based on the new data can be made either through the UI or a simple REST API call.
Cloud AutoML Vision is designed to offer machine learning models designed for an enterprise’s specific dataset. Currently, developers can use Google’s Cloud Machine Learning Engineer to access a pre-trained model or design and train their own custom model. Through Cloud AutoML VIsion, developers can classify images specific to their datasets. With Cloud AutoML Vision, a simple model can be created in minutes and more complex one in a day.
According to the Lis, accuracy is ensured in Cloud AutoML Vision by leveraging such Google image recognition approaches like transfer learning (using knowledge gained in one problem and applying it to another related problem) and neural architecture search technologies (for neural networks).




Be the first to comment